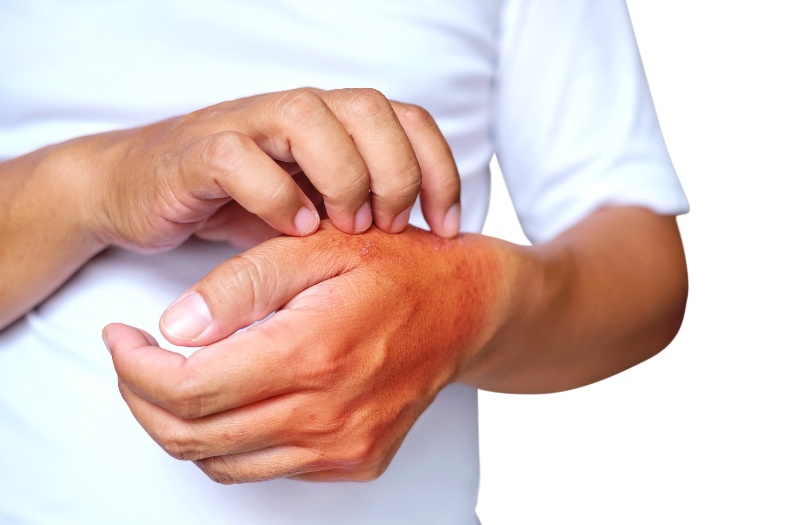
Millions of people suffer from dermatitis every day yet most people don’t know that it can be treated fairly easily with just a few changes. The first step is to even figure out whether you have dermatitis or some other underlying skin condition.
What is Dermatitis?
The phrase “Dermatitis” can be used to describe a number of conditions that affect your skin. Specifically, it refers to an inflammation that can be accompanied by irritations such as itchiness or a rash. Some of the more common examples are Dandruff (seborrheic dermatitis) or Eczema (atopic dermatitis).
The phrase itself is fairly self-explanatory, since “derm” refers to skin and “itis” refers to inflammation. While many cases can be mild, more severe breakouts can impact a person’s quality of life. That’s why it can be very helpful to arm yourself with the knowledge of what dermatitis is and how to treat it.
What are the causes and symptoms?
Because there are many kinds of dermatitis, the causes are fairly varied as well. Perhaps the most widespread source is contact with a certain substance. Others include your own immune system, allergies, or infection. Whatever the situation, symptoms can be difficult to live with.
As mentioned above, itchiness and rash are two symptoms that many forms of dermatitis share. Skin can flake up or feel cracked, and some severe cases can cause blood or other fluids to ooze from sores.
For the most part, dermatitis does not pose a significant risk to your health. It isn’t contagious, so you can’t spread it to other people. That being said, symptoms can be severely uncomfortable to live with, especially if left untreated. Thankfully, there are ways to mitigate the affects that the condition has on your body.
List of symptoms to look out for
If you have one or more of these symptoms, it could be an indication of dermatitis. Watch out for:
• Constant itching
• Red rashes on skin
• Dry or flaking skin
• Sores with fluid
• Rashes that bleed when scratched
• Ulcers
• Topical swelling
• Patches of scaling, hardened, or crusting skin
• Burning sensation on skin
The types of dermatitis
Among the types of dermatitis are:
• Atopic Dermatitis
• Allergic Contact Dermatitis
• Diaper Dermatitis
• Dermatitis Herpetiformis
• Dyshidrotic Dermatitis
• Irritant Contact Dermatitis
• Neurodermatitis
• Nummular Dermatitis
• Perioral Dermatitis
• Seborrheic Dermatitis
• Stasis Dermatitis
Who is vulnerable to dermatitis?
Because contact dermatitis happens through touch, pretty much anyone can contract it. With the other types, it just depends on what can cause symptoms. Diaper dermatitis obviously only happens to those that wear diapers. For something a bit rarer, dermatitis herpetiformis is more likely to occur with people with celiac disease. Examining the numbers, atopic dermatitis affects 2-3% of adults and 25% in children. While the likelihood of contact dermatitis varies based on occupation, it is estimated that 15-20% of all people will contract it at some point.
Read ahead for a list of causes for different forms of the condition.
Atopic Dermatitis:
• Usually begins in childhood
• Is likely to run in the family
• Incidents of familial hay fever or asthma can cause it
• More likely to effect females
• More likely to effect African-American children
Allergic/Irritant Contact Dermatitis:
• Affects those that frequently work around chemicals that are known irritants
• Affects those that frequently touch metals that are common allergens, like nickel and chrome
Periorificial Dermatitis:
• Occurs mostly in young adult women
• Can be triggered by steroid creams or inhalers
• Can be common with those who suffer from acne or rosacea
Dyshidrotic Dermatitis:
• Can affect people who sweat a lot
• Can affect people who let sweat sit on the skin for long periods of time
• Is more likely to occur in warm and humid areas
Other general causes
• An overactive immune system will cause your body to react negatively to minor irritants. Inflammation is a defense response, and it can occur sometimes even if there is nothing to defend against.
• Since dermatitis is tied to allergies and allergies are often hereditary, there is higher chance to contract it if your family has it as well.
• The use of cosmetics and other beauty products can lead to dermatitis because of the high amounts of possible allergens that are used in manufacturing. This can be from certain fragrances, the preservatives used in creams, or dyes and other colorings added to products.
Testing for dermatitis
Certain forms of dermatitis can be identified by a medical professional by examining the affected area. With other types, certain tests can assist in the identification process.
• Due to other conditions sharing symptoms with dermatitis, blood tests can determine if those are the cause instead of dermatitis.
• Skin biopsies can be employed to narrow down a specific form of dermatitis.
• Patch testing/allergy skin tests can see if a particular substance or chemical is causing symptoms.
Treating Dermatitis
To treat dermatitis, consult with your general practitioner or a specialist. Following their instructions is paramount to keeping flareups from happening. In addition, you’ll want to prevent coming into contact with whatever is causing your symptoms. It’s important to remember that this can extend past allergens. Anxiety can actually cause your body to become inflamed easier.
When prescribed a medication, be sure to complete the entire dosage. If you stop just because your symptoms get better, it increases the chances of the condition re-emerging later. There is also a number of precautions you can take by yourself.
• Manage Stress: As detailed above, anxiety can cause inflammation. Any activity that helps you calm down may benefit your skin. If you are finding it difficult to do this by yourself, you may want to consider speaking with a therapist.
• Avoid Hot Showers: Hot water will dry out your skin, causing more irritation and itching. This doesn’t necessarily mean bathing in cold water though. Lukewarm temperatures should be fine.
• Using Mild Soap: While bathing, use soaps that are designated as mild. These are less likely to irritate your skin since they avoid strong chemicals and fragrances.
• Using Moisturizers: As soon as you finish a shower, applying a moisturizer will keep your skin from drying out.
• Avoid physical irritants: Scratching is the most obvious thing to watch out for, but mind your clothes as well. Rough fabrics will irritate your skin as they move across it.